Crossover Component
The Crossover Component divides the audio input signals into 2 to 6 frequency bands for distribution to the appropriate loudspeakers for each band. In the default mode, there is a low-pass filter on the lowest band, and a high-pass filter on the highest band. You can choose up to 4 band-pass filters between the highest and lowest band. Both the highest and lowest bands have the option to become band-pass filters. You can choose the Slope rates and filter types (Butterworth, Linkwitz-Riley, Bessel-Thomson, Chebyshev) for each filter in each band.
The Crossover Component is capable of up to 256 channels and 6 Bands. Refer to the Properties table below for complete capabilities. You can create and configure as many crossovers as you need.
Note: The number of signal pins is variable and set in the component's Band CountProperty.
Input Pins
Input
Audio signal pins are represented by a (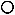 ) circle, and traditional wiring is represented by a thin black line. You can use Signal Names on audio signal pins.
) circle, and traditional wiring is represented by a thin black line. You can use Signal Names on audio signal pins.
By default, the Crossover component is set to a 2-waychannel, which provides 1 input and 1 output. Additionally, you can set the Properties to allow for 3-way, 4-way , 5-way, or 6-way,which gives you 1 output channel for each band.
Output Pins
Output
Audio signal pins are represented by a ( ) circle, and traditional wiring is represented by a thin black line. You can use Signal Names on audio signal pins.
) circle, and traditional wiring is represented by a thin black line. You can use Signal Names on audio signal pins.
By default, the Crossover component is set to a 2-waychannel, which provides 1 input and 1 output. Additionally, you can set the Properties to allow for 3-way, 4-way , 5-way, or 6-way,which gives you 1 output channel for each band.
Crossover Properties
Max Slope
Controls the maximum slope you can apply to a band. The Slope settings in the Control Panel are set by default with a range of 6 dB per octave, to 48 dB per octave.
Band Count
Band Count controls the number of frequency bands you have in the crossover component. For every input channel, there is one output channel for each band. For example, two input channels, four bands = eight output channels.
High-pass Low Band
Determines if the lowest band has a high-pass filter or not.
Low-pass High Band
Determines if the highest band has a low-pass filter or not.
Channels
Type
Sets the type of input/output channels. You can choose Mono, Stereo, or Multi-channel depending on the input type of your Crossover.
Response Panel
Enabled
Enables the graphical Response panel in the Control Panel.
Size
Adjusts the size of the Response panel.
Graphic Properties
Label
Use the Label property to change the name of the component in the schematic. The Label property defaults to the component name. To learn more about renaming schematic elements, see Organizing Your Design.
Position
The coordinates reference a specific place in the schematic - for example,"100,100" (horizontal, vertical). 0,0 is the upper left corner of the schematic.
Fill
Sets the fill color of the component in the schematic.
Script Access Properties
Code Name
Displays the currently assign name for control access. You can use the auto-assigned name or customize it. Q-SYS will automatically check all Code Names in the design to ensure name is unique.
Script Access
Defines whether the component will be accessible by script and/or externally, or not at all. Choices include All, External, None (default), and Script.
Tip: Use Script Programmer Mode to quickly view the Script Access setting directly on the component in the design schematic without the need to disconnect from the Q-SYS Core processor.
Response - All
Turns the all individual band crossovers and slopes on and off.
Response - Phase
Turns the phase graphic on or off.
Invert
Inverts the polarity of the output signal for the associated band.
Mute
Mutes the output for the associated band.
Gain (dB)
Adjusts the output gain for the associated band.
Frequency (Hz)
Determines the frequency the band will start (high-pass) and stop (low-pass) passing the audio signal. The low-pass frequency of a band cannot be lower than the high-pass frequency of the same band - the high-pass frequency will automatically adjust lower.
Slope
Determines the rate of change of attenuation at the high-pass and low-pass frequencies of the band. The slope setting establishes the crossover region between two adjacent bands. The available Slope settings depend on the choice made in the Crossover Properties Max Slope.
Type (dB / Octave)
The Type setting includes: Butterworth, Linkwitz-Riley, Bessel-Thomson, Chebyshev filters. You can select any combination of two of these filters for a band's high-pass and low-pass frequencies. When you choose Bessel-Thomson, you are given the option of various types of normalization.
Bypass
The Bypass button is available only on the highest and lowest bands, and only when High-pass Low Band and Low-pass High Band options are chosen in the Crossover Properties. The Bypass button bypasses the high-pass filter for the lowest band, or the low-pass filter for the highest band. Basically, it makes it as if you had not selected the High-pass Low Band and Low-pass High Band options.
Bessel Normalization
Selects the type of normalization for the High-pass and Low-pass Bessel-Thomson filter.
Link
The Link button links the high-pass frequency control of a band to the low-pass frequency control of the adjacent lower band. The two controls are synchronized, and controlled by the low-pass knob in the lower band. This makes it easier to keep two adjacent bands' crossover region in sync.
The available Control Pins depend on settings in Properties.
Each band in the Crossover can have High and Low settings. The following table lists the duplicated settings only once.
|
Pin Name |
Value |
String |
Position |
Pins Available |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Gain |
-100 to 20 |
-100 dB to 20 dB |
0.000 to 1.00 |
Input / Output |
|
Bypass |
0 1 |
active bypass |
0 1 |
Input / Output |
|
High or Low Frequency |
10.0 to 20,000 |
10 Hz to 20 kHz |
0.000 to 1.00 |
Input / Output |
|
High or Low Normalization |
0 1 2 3 |
-3 dB Flat Group Delay -3 dB Mirror Magnitude Natural Mirror Magnitude Natural Phase Match |
0 .333 .667 1.00 |
Input / Output |
|
High or Low Slope |
6.0 12.0 18.0 24.0 30.0 36.0 42.0 48.00 54.0 60.0 66.0 72.0 78.0 84.0 90.0 96.0 |
6 dB/Oct 12 dB/Oct 18 dB/Oct 24 dB/Oct 30 dB/Oct 36 dB/Oct 42 dB/Oct 48 dB/Oct 54 dB/Oct 60 dB/Oct 66 dB/Oct 72 dB/Oct 78 dB/Oct 84 dB/Oct 90 dB/Oct 96 dB/Oct |
0.00 .067 .133 .200 .267 .333 .400 .467 .533 .600 .667 .733 .800 .867 .933 1.00 |
Input / Output |
|
2 3 4 5 |
Butterworth Linkwitz-Riley Bessel-Thomson Chebyshev |
0 .333 .667 1.00 |
Input / Output |
|
|
Band Invert |
0 1 |
normal invert |
0 1 |
Input / Output |
|
Band Link |
0 1 |
enable disable |
0 1 |
Input / Output |
|
Band Mute |
0 1 |
unmute mute |
0 1 |
Input / Output |
|
Master Gain |
-20 to 20 |
-20 dB to 20 dB |
0.000 to 1.00 |
Input / Output |
|
Master Invert |
0 1 |
normal invert |
0 1 |
Input / Output |
|
Master Mute |
0 1 |
unmute mute |
0 1 |
Input / Output |
Using Components with Snapshot Controller Ramp Time
Components such as the Crossover Component or other Text Controller or Custom Controls like the Integer Knobs, and Hexadecimal Knobs will not be recalled by Snapshot if the Ramp Time is a non-zero number.
